- Herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), also known as the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14 (TNFRSF14), is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor family, which defined structurally by multiple, extracellular, and cysteine-rich domains (CRD). HVEM activates NF-κB pathways through interaction with multiple TNF receptor-associated factors (TRAFs).
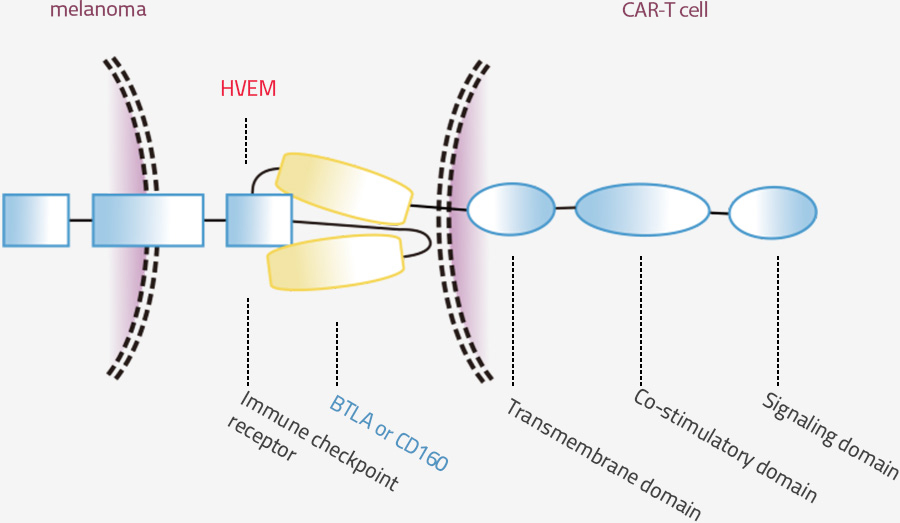
- HVEM is expressed in a variety of immune cells including T cells, B cells, natural killer cells, dendritic cells, and endothelial cells. It is also known as one of the checkpoint receptors like PD-1, CTLA4, B7-H3, and etc. HVEM has a role for immune evasion of tumors through frequent expression on melanoma cells. HVEM is considered a good target for CAT-T treatment for melanoma.
- BTLA and CD160 act as an immune suppressor through its interactions with HVEM. It is expressed on natural killer (NK) cells and both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. The extracellular domain of BTLA and CD160 bind directly to HVEM. Our research team produces BTLA and CD160 CAR-T construction for the connection of HVEM. BTLA or CD160 CAR-T can interact with HVEM expression melanoma cells and kill them.

